Understanding Bitcoin Mining Difficulty and How to Calculate It

Introduction
Bitcoin mining is a complex process that involves solving cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and secure the Bitcoin network. The difficulty of these puzzles, known as mining difficulty, plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and security of the Bitcoin blockchain. As the Bitcoin network grows, the difficulty adjusts to ensure that blocks are mined approximately every 10 minutes. This article will explore what Bitcoin mining difficulty is, why it’s important, and how it is calculated.
What Is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty?
Bitcoin mining difficulty is a measure of how challenging it is to find the correct hash for a new block. The hash is a specific number that miners must discover by solving complex mathematical puzzles. The higher the mining difficulty, the harder it is to find this number, and the more computational power is required to mine a block.
Mining difficulty is designed to adjust automatically to the total amount of computational power (hashrate) on the network. This adjustment ensures that new blocks are added to the blockchain at a consistent rate, regardless of how many miners are participating or how powerful their hardware is.
Why Is Mining Difficulty Important?
Mining difficulty plays several vital roles in the Bitcoin network:
- Maintains Block Time Consistency:
Bitcoin’s protocol is programmed to produce a new block every 10 minutes. The mining difficulty adjusts to ensure that this time remains consistent, even as more miners join the network or mining hardware improves. Without difficulty adjustments, blocks could be found too quickly or too slowly, disrupting the flow of transactions and the reward distribution process. - Network Security:
Difficulty ensures that mining is a resource-intensive process, which makes it harder for any single entity to take control of the network. If mining were easy, malicious actors could manipulate the blockchain by overwhelming the network with their computational power, leading to attacks such as double spending or a 51% attack. By maintaining a high difficulty, the Bitcoin network remains secure and decentralized. - Ensures Fairness:
Difficulty adjustments help keep mining fair for all participants by ensuring that no miner or group of miners can dominate the network. Even though some miners have access to more powerful hardware, the difficulty ensures that they must work just as hard to find blocks as everyone else.
How Is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty Calculated?
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty is recalculated approximately every 2,016 blocks, which equates to about every two weeks. This recalibration, known as a difficulty adjustment, is based on the total hashrate of the network and the time it took to mine the previous 2,016 blocks.
The goal of the adjustment is to maintain the 10-minute block time. If blocks were found faster than every 10 minutes during the previous period, the difficulty will increase, making mining harder. If blocks were found more slowly, the difficulty will decrease, making mining easier.
Bitcoin Difficulty Formula
The formula used to calculate the new mining difficulty after every 2,016 blocks is:
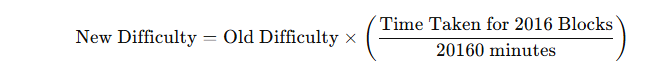
Where:
- Old Difficulty is the difficulty level for the previous 2,016 blocks.
- Time Taken for 2016 Blocks is the actual time it took to mine the last 2,016 blocks (in minutes).
- 20160 minutes is the ideal time it should take to mine 2,016 blocks (10 minutes per block for 2,016 blocks).
Example Calculation
Let’s say the previous difficulty was 10 trillion (10,000,000,000,000), and it took 19,440 minutes to mine the last 2,016 blocks (instead of the ideal 20,160 minutes). The new difficulty would be calculated as follows:
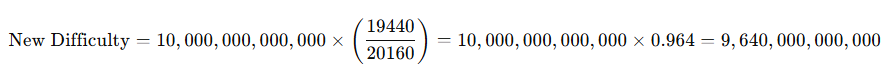
In this example, the difficulty decreases slightly because blocks were being mined faster than the 10-minute target.
Factors That Influence Bitcoin Mining Difficulty
- Hashrate:
The total computational power of the Bitcoin network, or hashrate, is the primary factor that influences difficulty. As more miners join the network or upgrade to more powerful hardware, the hashrate increases. To compensate for the added computational power, the difficulty increases, ensuring that block times remain stable. - Mining Technology:
Over the years, advances in mining technology have led to more efficient and powerful hardware, such as ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) machines. As these machines can solve cryptographic puzzles more quickly, they contribute to a higher overall hashrate, resulting in increased difficulty. - Network Participation:
When more miners participate in the network, the total hashrate increases, leading to a rise in difficulty. Conversely, if miners leave the network due to factors such as high electricity costs or unprofitable conditions, the hashrate decreases, and the difficulty adjusts downward. - Bitcoin Halving:
Every four years, Bitcoin undergoes a halving event, where the block reward (the number of new bitcoins issued for mining a block) is cut in half. While halving does not directly affect difficulty, it impacts the profitability of mining, potentially driving some miners to exit the market. As a result, this could cause the network’s hashrate to decrease, leading to a downward difficulty adjustment.
Difficulty and Profitability: The Relationship
Mining difficulty and profitability are inversely related. As difficulty increases, miners need to invest in more powerful hardware and consume more electricity to remain competitive. If the difficulty becomes too high relative to the Bitcoin price, mining can become unprofitable, especially for small miners or those without access to low-cost electricity.
Miners constantly evaluate the balance between mining difficulty, Bitcoin price, and operational costs (such as hardware and electricity) to ensure that their mining operations remain profitable.
How to Monitor Bitcoin Mining Difficulty
Monitoring Bitcoin mining difficulty is essential for miners to adjust their strategies and investments accordingly. Several websites and tools allow users to track difficulty changes and hashrate trends. Some popular platforms for monitoring difficulty include:
- Blockchain.com
- BTC.com
- CoinWarz
- WhatToMine
These platforms provide up-to-date information on the current difficulty level, historical trends, and predictions for the next adjustment.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining difficulty is a core aspect of the network’s security and stability, ensuring that blocks are mined at a consistent rate and that the network remains secure against attacks. As more miners join the network or leave due to changing profitability, the difficulty adjusts to maintain this balance. Understanding how difficulty is calculated and its impact on mining profitability is essential for anyone involved in Bitcoin mining.
By keeping an eye on difficulty trends, hashrate, and external factors like hardware improvements and Bitcoin price fluctuations, miners can make informed decisions on how to adjust their operations to maximize efficiency and profitability.
This article presented by Loka Mining.
Loka is revolutionizing the Bitcoin mining ecosystem by directly connecting investors with Bitcoin miners through a decentralized mining pool and an upcoming permissionless forward hashrate marketplace protocol.
Loka enables investors to get Bitcoin at lower than market price without centralized & counter-party risks, and Bitcoin miners to access capital efficient financing and hedge their risk exposure by selling their future mining rewards.
Find out more about loka in https://lokamining.com — or access our mining pool aggregator on https://pool.lokamining.com




